Browser
Browser is a software application for gettig access to different content on the Internet (World Wide Web). Modern browsers are potent of bringing web pages, images, videos and content of other types to the user.
History of a web browser
The first web browser, named WorldWideWeb, was launched already in 1990. Later on, it was renamed into Nexus for disambiguation purposes. The first browser to have a graphic user interface (GUI) was Mosaic, which was a breakthrough back in 1993. Browsers have evolved a lot since then: some of them became prominent, some fall into oblivion.
How does a browser work?
The main aim of a web browser is to bring the needed information to the user, present it, and allow navigating to other pages and websites on the net. All starts with a URL (Uniform Resource Locator), or, simply, a link, entered into the browser address bar. A link should start with a transfer protocol: HTTP, https, FTP or file for local files. After this, the web browser renders the HTML page, as well as CSS, JavaScript content, images, videos, audios and XML files, associated with it. The user may click on links to continue browsing.
What are most popular modern browsers?
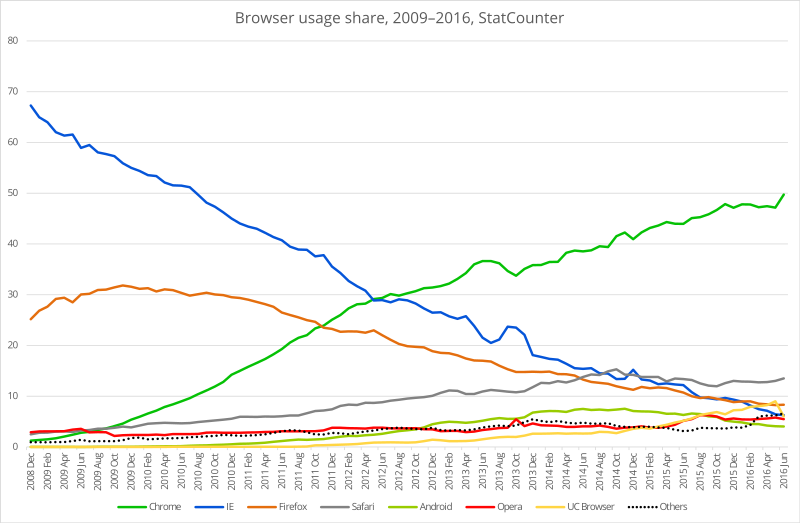
StatCounter reports that the most popular modern browser is Google Chrome, with 62% market share. The runner up is Mozilla Firefox with 14.81% market share. Other popular browsers include Internet Explorer, Safari and Microsoft Edge.
Browser functionality
The common set of browser interface elements include buttons, such as home, back, forward, and refresh, as well as other elements, such as address/search bar, viewport, and the status bar that displays loading progress.
Modern web browsers offer rich user interfaces and allow working with different file formats and protocols. Some of them block pop-up windows, have inbuilt PDF readers, allow working with documents, spreadsheets, etc. Moreover, the user can extend modern browsers with plugins and extensions that provide for some specific user’s needs.
Cross-browser compatibility
When launching a website, the website owner should make sure that their website displays equally well in different modern browsers. This process is referred to as cross-browser testing. The procedure is rather painful, as tweaking cross-browser display differences is a tedious procedure.
You should account for cross-browser compatibility on different stages of website creation. If you use a template for website creation, choose the one produced by well-established template providers. For instance, you make check modern cross-browser compatible templates by TemplateMonster. Check their WordPress themes in different browsers, and you’ll see that they look exactly the same.
Moreover, make use of Online Tools to check your website browser compatibility, and be confident in your website display in all modern browsers.
Related terms: URL, HTTP, HTML, website, web page, bookmark, cookie, application.
References and further reading:
- Web browser – Wikipedia.
- Web browser. Definition and basic information.
- Browser. A short history of browser software development.