How can I customize my WordPress site?
Once your WordPress engine is successfully installed, you’ve already made good progress. Still, there is plenty left to learn. I’m going to go through the functions and features that are prepackaged with the WordPress engine. Just remember that you can improve on them with plugins, frameworks and themes.
You’ll Learn About:
The tools to create and edit content in basic WordPress are pages, posts, categories of posts, widgets, menus and comments. Of course, there are some “Easter eggs” hidden here and there. We’ll touch on those later as well.
1. Content management
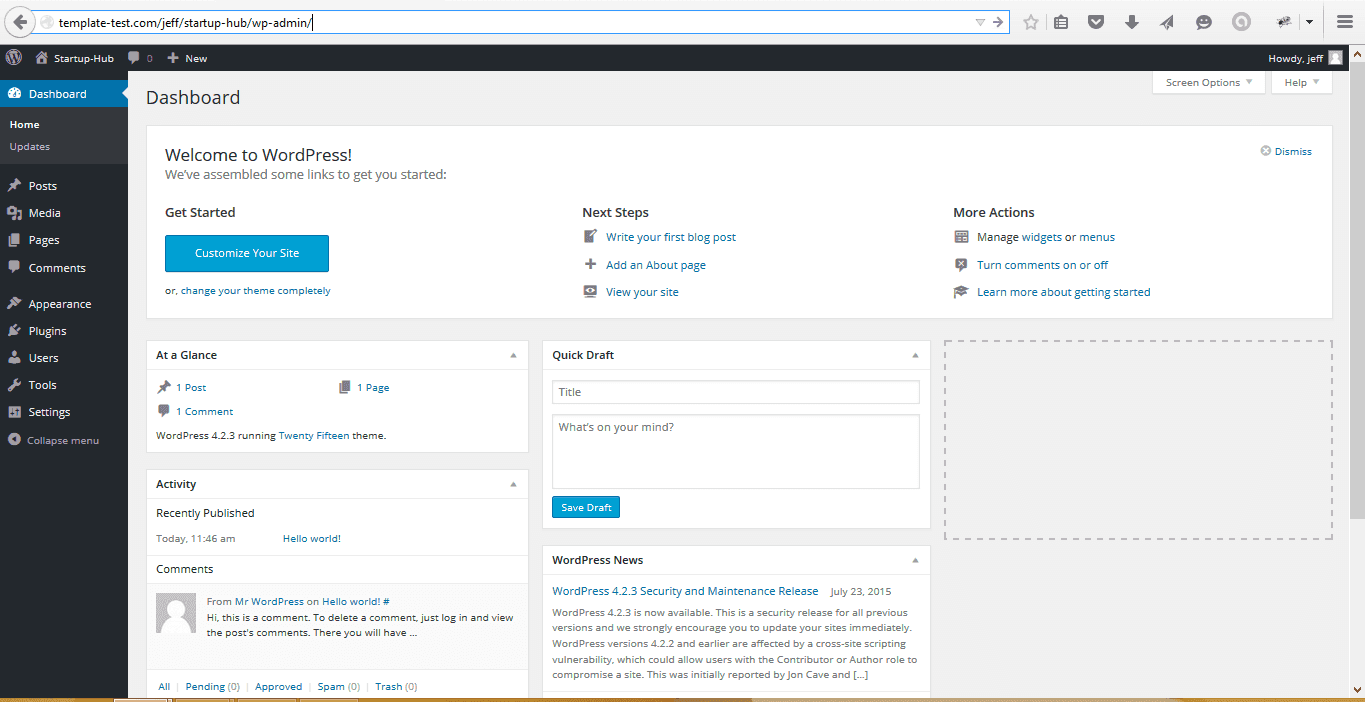
Dashboard
The WordPress engine admin panel is called the Dashboard. You can always access it by adding /wp-admin or /wp-login.php to your site url. Using your dashboard, you can manage most of your site content and media.
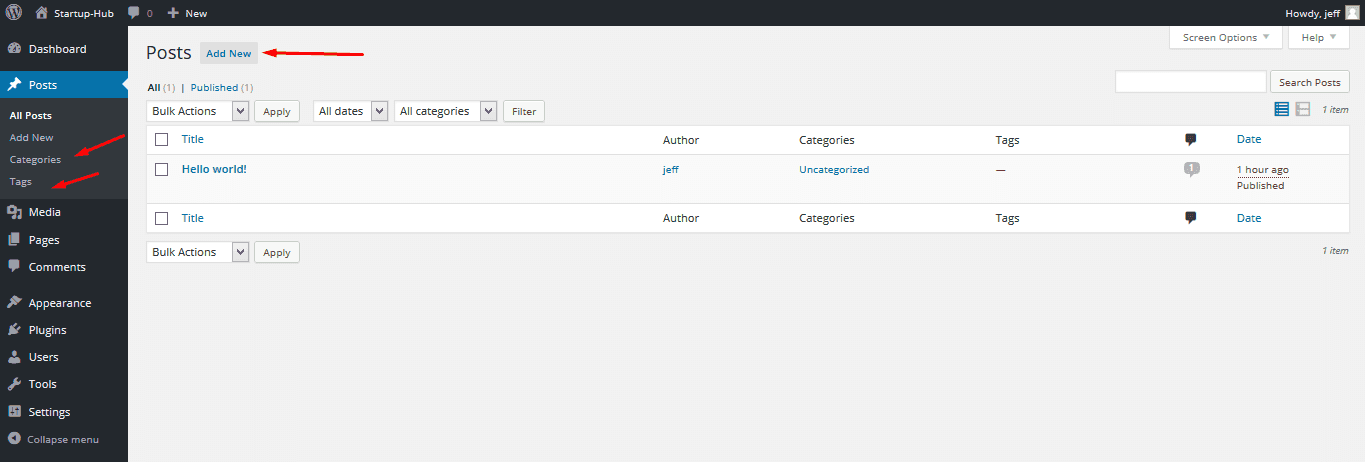
Posts
The main reason people install WP is to post their custom content. Posts in this engine are the smallest content units with which you can work.
When you open the Posts tab on the left of your Dashboard, you see all the posts you have on your site. When editing a post, you can choose one of the post types in the panel on the right, for example, “gallery” or “quote”.
In the post content window, you can add texts and media. There are two editing formats available - Visual and Text. The visual mode will be perfect for beginners. However, if you know a little HTML, try switching to the Text mode where you can fine-tune the format with HTML markup.
If you wish to see how your work looks on the front-end, you can click on the Preview button to see it. If you accidentally saved the unwanted changes, you can always restore the previous revision of your content. In the panel on the right, you can also add tags and assign posts to certain categories.
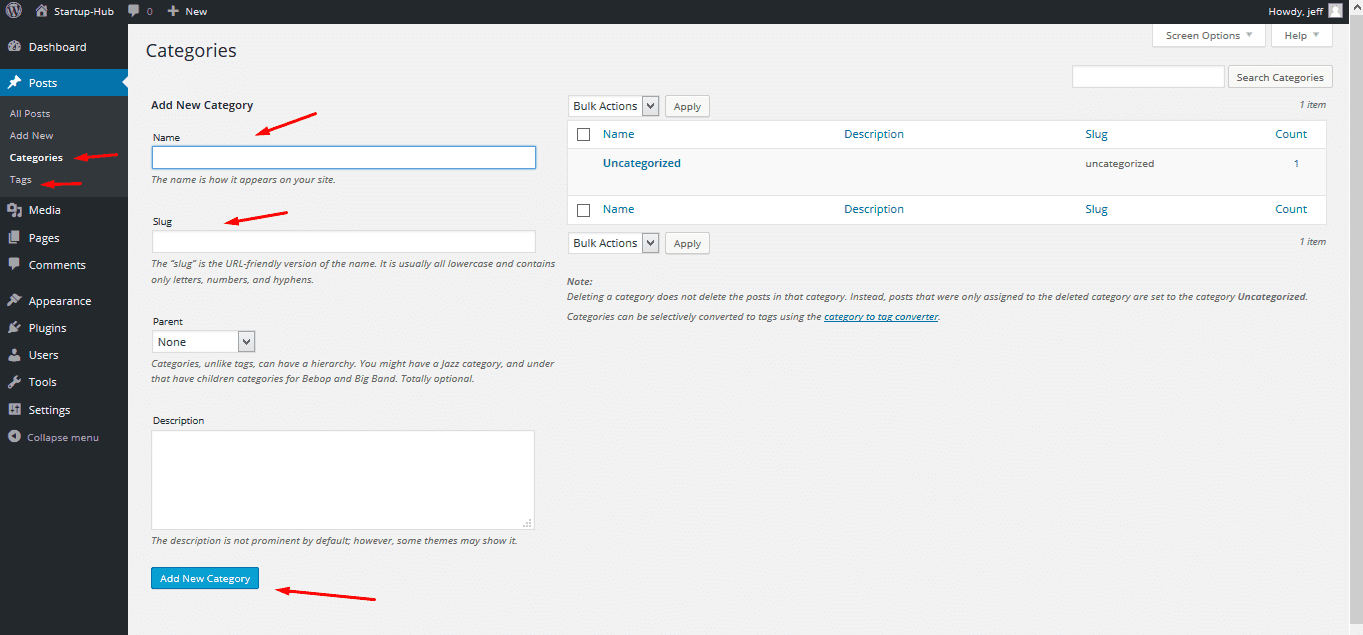
Categories
You can locate your categories in the dashboard if you hover over Posts. In the drop-down menu next to it you’ll see Categories. The Categories section lets you group your posts by topics.
You can create any number of categories and assign posts to one or more of them. If you want to display posts from a certain category on a separate page of your site, you can add that category as a menu item, or access it directly with a URL which looks like this: http://www.name-of-your-site.com/category/name-of-the-category/
Categories is a cross-platform tool. Learning to use categories in WordPress can also help you in working with other platforms like Joomla.
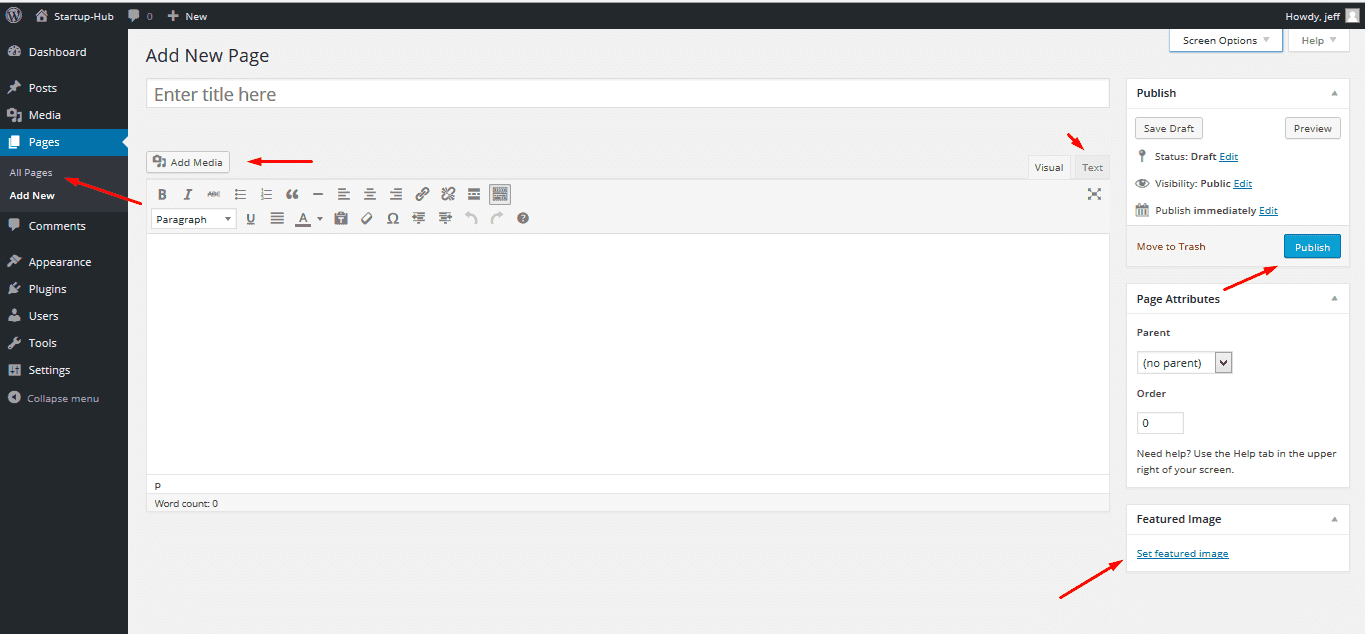
Pages
The Pages section of your Dashboard is the one you use to create static content for your site. A typical site has about 5 main pages: Home, About, Blog, Contact, Services (Portfolio). If you use a template with sample data, these usually come included. It's easy to notice that pages are a lot similar to posts, but they do have several very important differences:
- Pages don’t have categories or tags
- You can display posts on pages but not the other way around
- Pages can be a child or a parent to other pages. That helps inherit the settings
- Pages have an option to change page template, which defines what the page displays and what it will look like
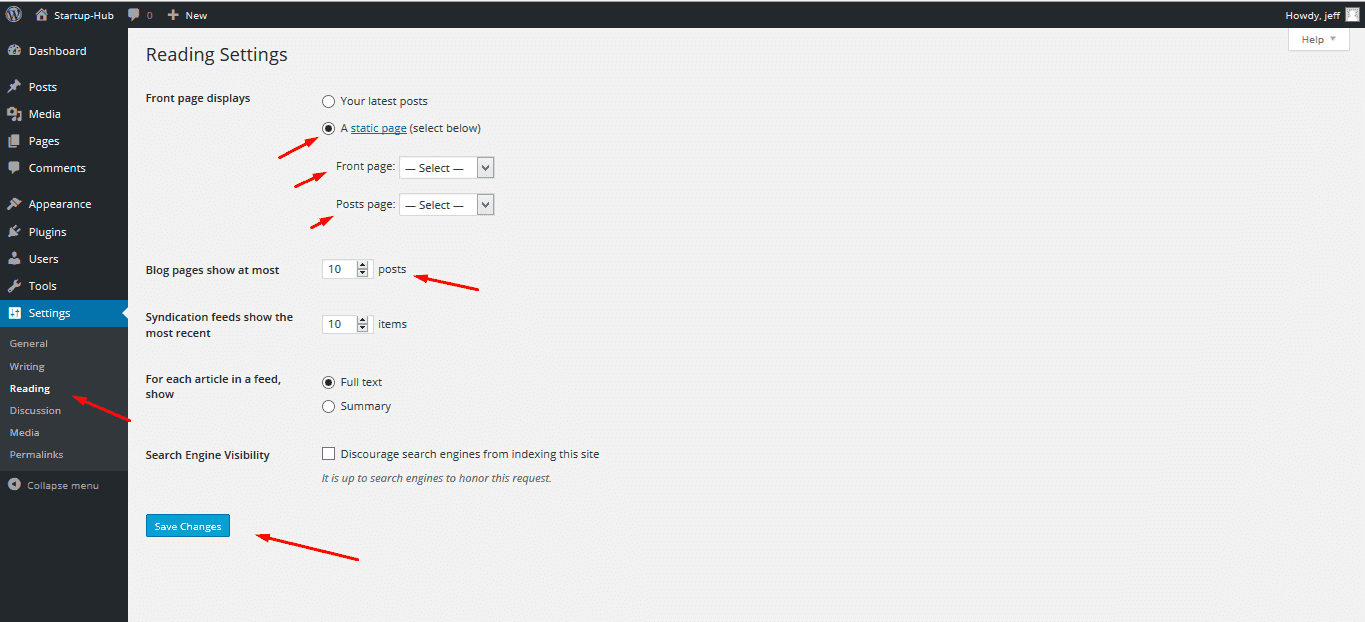
In the Settings-> Reading section of your Dashboard you can choose your Homepage and Posts page. Tick the static page option and choose the Front page and Posts page. The first one will show up each time someone opens your site url, the second is the page that will display all of your posts.
Menus
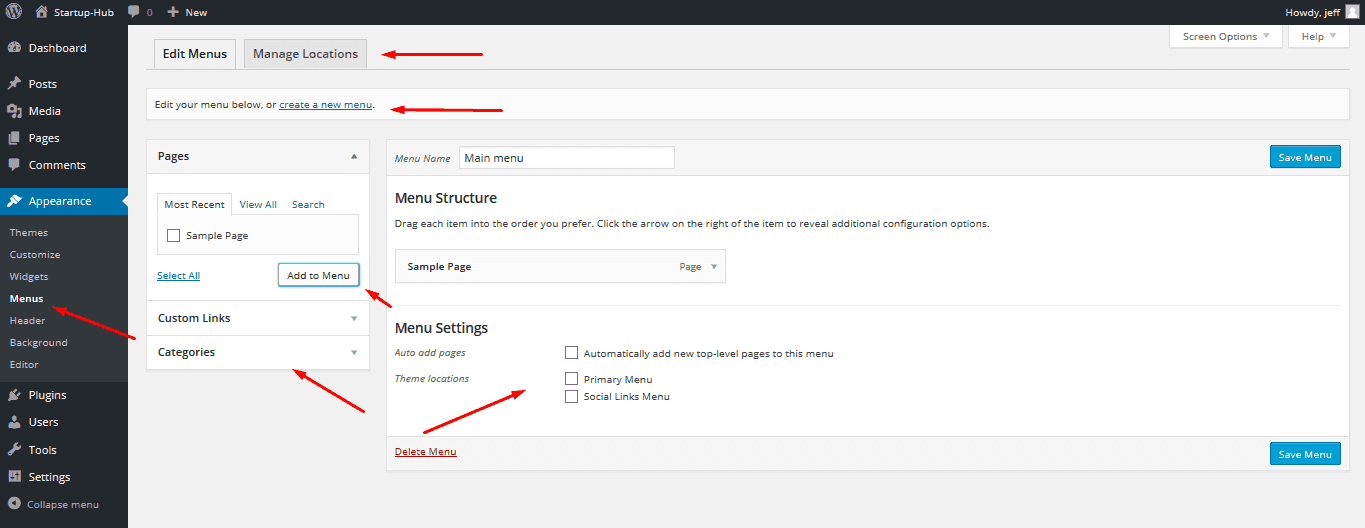
The first thing a visitor looks for on a site is the navigation menu. Menus in WordPress are easier to manage than in any other popular CMS engine. In the Appearance -> Menus section of your Dashboard, you can edit the existing menu items, add new ones or create new menus from scratch. The good news is that you can add not only pages to your menus, but categories and custom links as well.
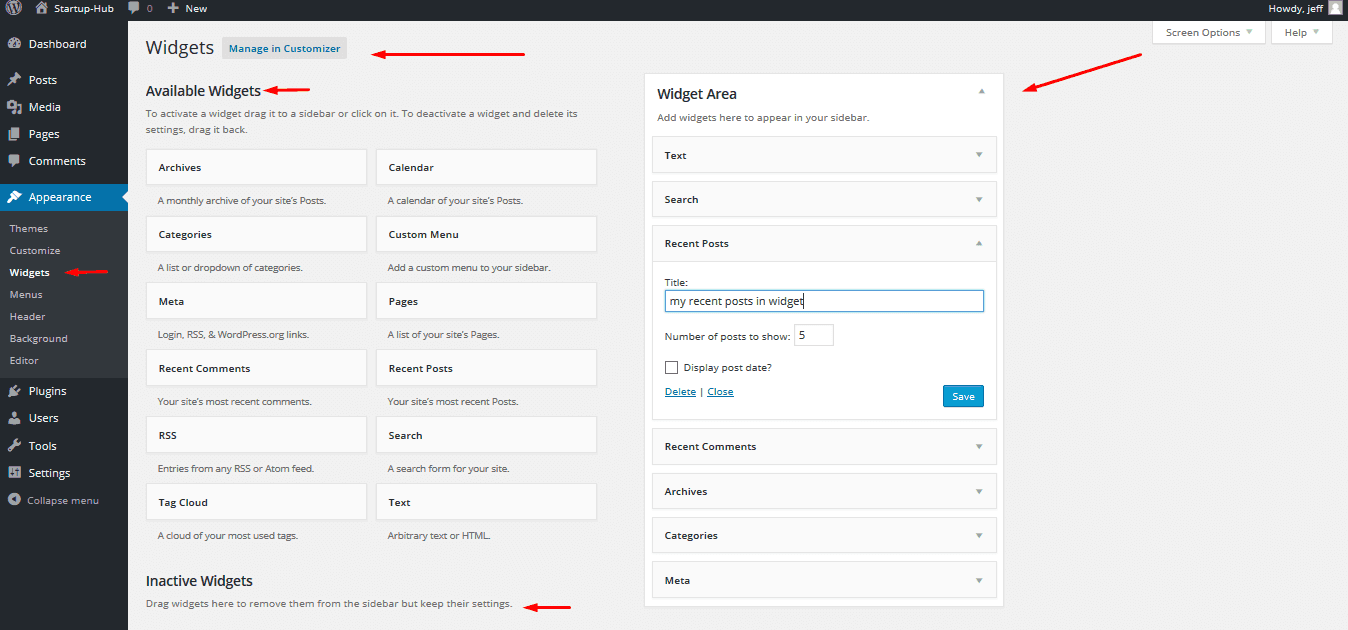
Widgets
Most commonly, Widgets are located in the sidebar of your WordPress pages.
Usually the content takes three quarters of the page width and the sidebar is located on the right or left of it. Sidebars contain additional info you might need: site map, archives, search bar, recent posts, text or images - anything you want, but small.
You can also display widgets in custom added widget areas on your pages. They can be located in your site’s header or footer. With the help of plugins you can make widgets appear anywhere on your site if needed.
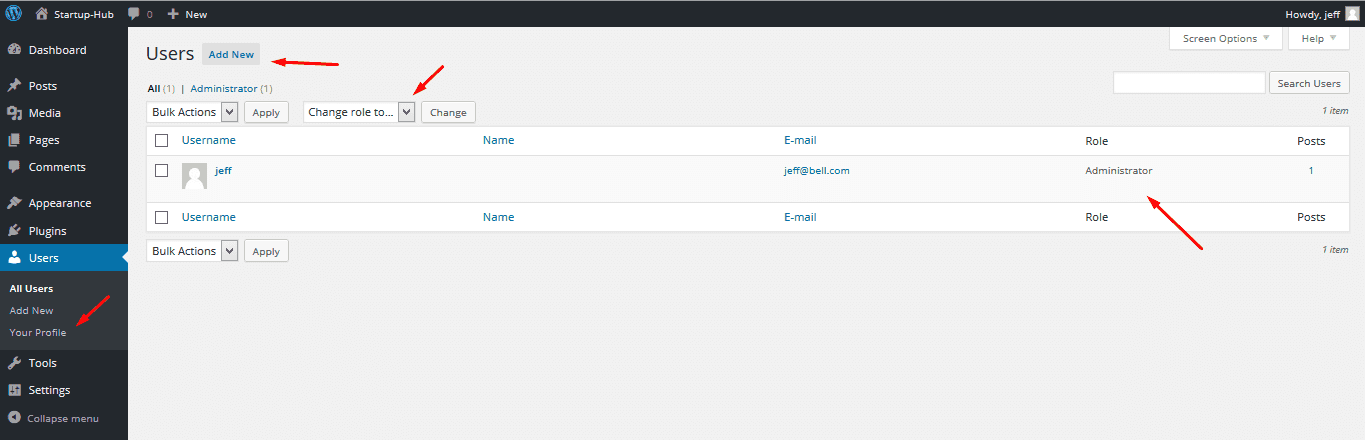
Users
WordPress provides you with an option to let other people sign up on your site and share their content. You can disable this feature at any moment.
If you want to keep it and take advantage of it, you can manage the roles and capabilities of Users in your dashboard. WordPress lets you change the user roles yourself and give certain logged in customers more or fewer rights for adding their content to your site.
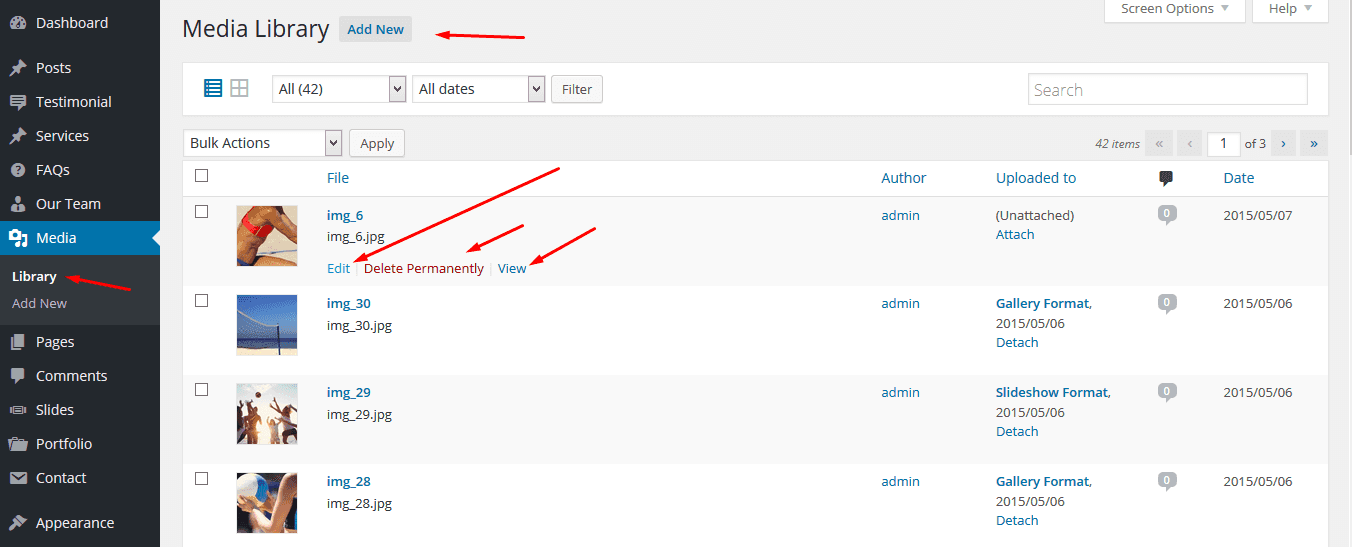
Media library
One more special thing about WordPress is how easily you can access your site media. In the Media -> Media library section you can access images, videos and audio files on your site.
These files will appear in the Media library after you’ve uploaded them as a part of posts or pages (using the “add media” button). Click on any of them to get a direct URL of the file, to edit its title, alternative text or description.
2. Design and custom functions
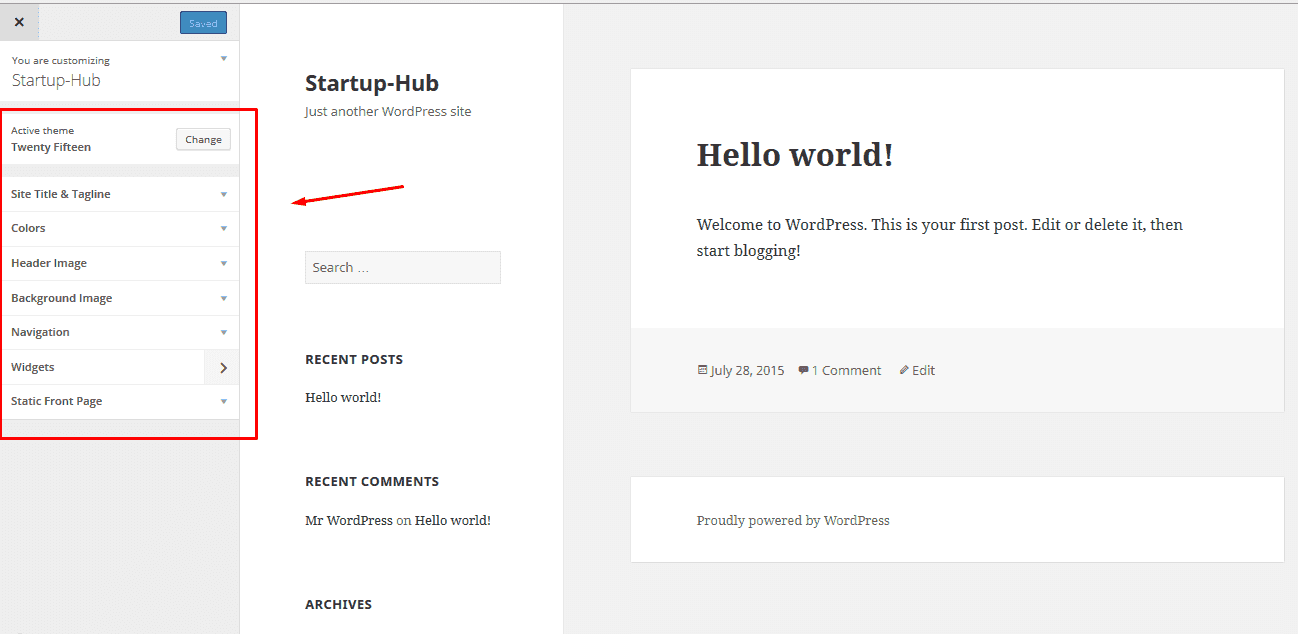
Customize
In WordPress, you can change the layout, colors, some backgrounds and fonts in the Appearance -> Customize section of the admin Dashboard.
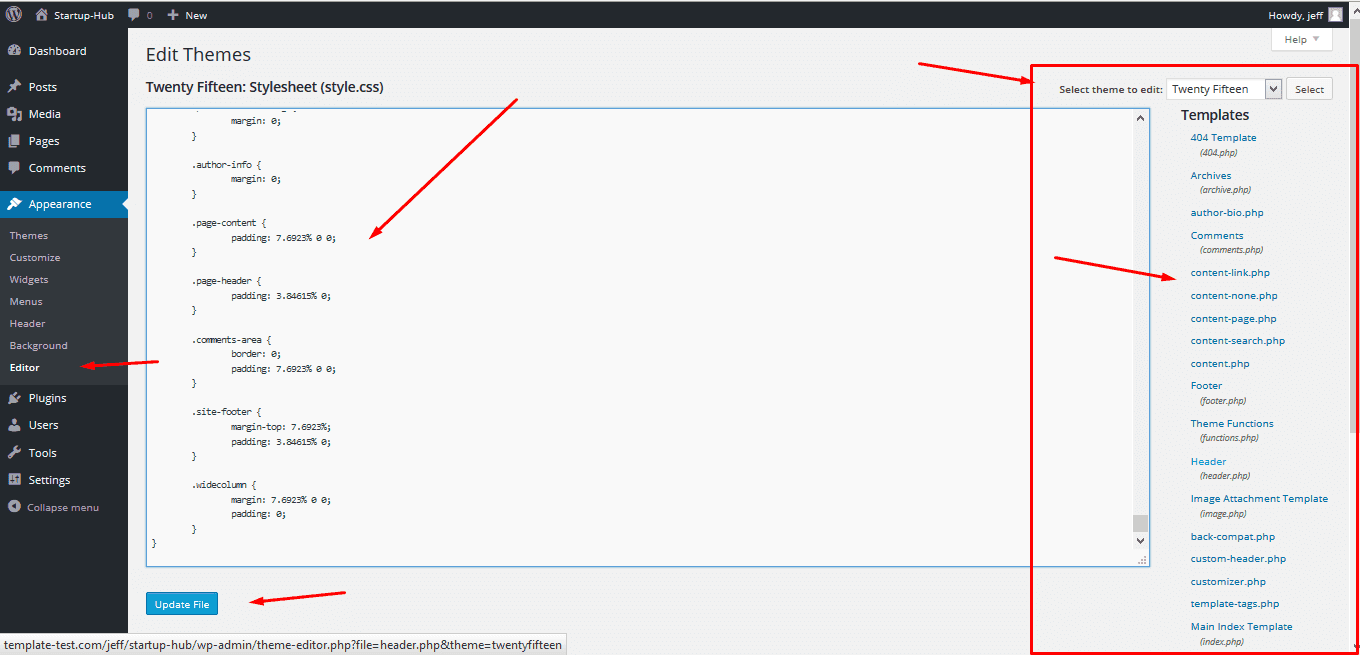
Editor
If you’re familiar with CSS or PHP, WordPress provides you with an option to edit them from the admin Dashboard, which is a rare benefit among the site engines. You can locate some of your site files in Appearance -> Edit. Even a beginner can use these files to make some changes, for example, change the color scheme.
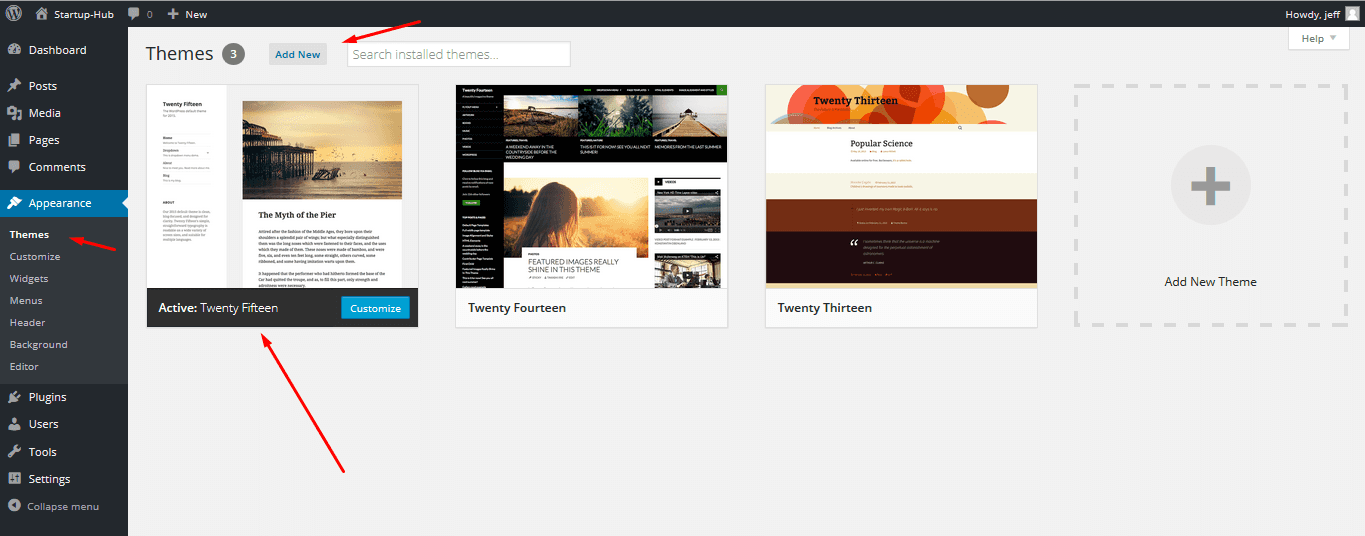
Themes
Themes or templates are ready-made design solutions for your site. When you install a theme, either free or premium, your site gets a different enhanced look. You can have several themes uploaded at the same time, but only one can be activated.
To upload a new template or activate another one, you need to navigate to the Appearance-> Themes section of your Dashboard. Check the guide on theme installation here.
3. Custom functions in templates for WordPress
You can always tell when a website runs the default WordPress theme, even if it’s customized and improved with plugins. If you are building a site just for fun, that’s fine, but if it’s a site for your business, consider using a theme from some template provider. That will bring credibility to your website’s look.
The advantages of using a theme are not limited to the visual perks - a beautiful non-standard color scheme and layout, or with the images included. A good theme will also have specific custom functions. For example, a template for recruiting agencies will include the custom post type “vacancies” and a working form to submit a CV.
Before installing a free template or purchasing one for your site, contact the template provider and figure out all of the details about it:
- for what versions of WordPress is the template developed? (some themes are developed for specific releases only, which will make any updates dangerous)
- what additional features are included in it?
- what kind of documentation comes with the theme?
- is the template “responsive” – i.e. mobile-friendly?
- are custom layout options available?
- what is the list of compatible and recommended plugins?
- is there tech support for the product you’re getting (live chat support in particular)?
Conclusion
Working with WordPress is fun and easy once you give it a try. It gets more and more intuitive and user-friendly with the release of each new version. In this guide, we’ve covered the most widely used WordPress features and Dashboard options. But it doesn’t end there. Even if you work with this platform for a long time, it will sometimes surprise you with what it can do. If you need technical help with WordPress maintenance service, don't hesitate to contact WPBuffs.
Now you know how to customize your WordPress Dashboard and are aware of what important functions come included with it. If you have any further questions, feel free to contact us, just click the red button above. If you have advice to help new users, please share it in our comment section below. If you would like to get more info on how to work with your site, feel free to subscribe to our updates.
Now that you know how to customize your site, you're ready to get an awesome WordPress theme and start blogging like a pro.
Jeff Bell
Jeff is a 20 year old Tech Support Operator at TemplateMonster. Helping our clients to edit and customize their sites every day, he knows what they need most and how to make it as easy as possible. More than one satisfied client already promised to call their child after him. Being a semi-professional high jumper in the past Jeff leaves no issue unresolved.