What are Gestalt Principles and Why You Should Care About Them
- Why you should care about gestalt principles
- Figure-ground
- Similarity
- Proximity
- Continuity
- Closure
- Focal Point
Why you should care about gestalt principles
Our brain always wants to us to see things the way they are, but our critical judgment helps us analyze the world and see it from different angles. The brain works on finding structures, patterns, and logic in every object.
For example, look at this picture:

First, you should know that there are two animals that you can see there: a duck and a rabbit. Let’s say that first, you see the rabbit, what happens next?
That’s right; we start analyzing the shapes we see and try to make sure that rabbit is the only creature that we should see in this picture. Our eye keeps looking at all the details and one moment you see that there is also a duck drawn on the picture.
If you are an experienced designer or a creative mind, you’ll ask yourself a question: damn, is there a way to use this trick in my designs? And the answer is ‘yes,’ so let me show you what the principles that you can apply to your design work are and how you can use this kind of a trick to make your designs more appealing.
There are three ways gestalt principles may influence your web design templates:
- They will help you make your designs more efficient and interactive. You’ll know when you should use hierarchy or background shading. You’ll understand how to group objects on the screen correctly.
- You will be able to direct users’ attention to a specific point of focus and make them take specific actions, behave as you need.
- Gestalt principles will help you design the product that will solve users’ problems most efficiently and attractively with the intuitiveness and user-friendliness applied.
What are the main gestalt principles? Let’s look!
Figure-ground
This principle states that our mind believes that every object should be either on a background or in the foreground, so every picture is analyzed by our brain this particular way. For example, let look at the picture below.

It’s evident that there is a tree drawn here, but if you take a more in-depth look, you’ll see that the tree is located on the background while there are a chimp and a tiger on a foreground. Two opposite colors help the author of this picture to make it possible for our brain to break down this picture into the separate elements.
Here is a real-life example of how the figure-ground principle can be used:

This is a Formula 1 logo, and you can see an ‘F’ here and then a red area symbolizing the high speed. But when you look closer, you note the ‘1’ sign.
Similarity
This principle states that we tend to group all the elements that look similar or the same to our eyes. For example, in this picture, you can see that there are two separate groups of shapes: triangles and circles.
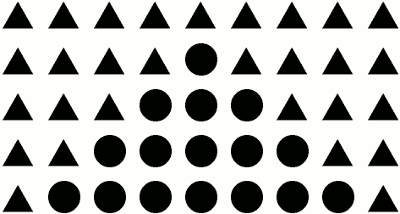
Our brain automatically thinks that these two groups have entirely different functionalities and purposes.
That’s one of the most popular principles applied in UI design when we work on different forms, applications and other grid-related things. Here is an example, so you could see what I’m talking about:
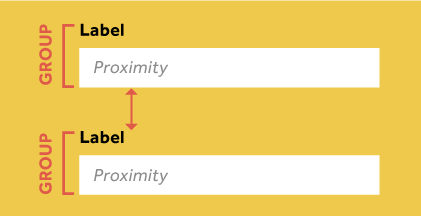
Proximity
This is probably the easiest and most obvious statements. All the objects that are located closer to each other appear to be more related than the ones that have a considerable amount of space in between.

When you design user interfaces, you should always understand how to highlight that a specific field is connected to the button or a placeholder. This is where the proximity comes in and helps you influence the users’ understanding of how to interact with your design.
Continuity
Continuity defines that elements that are aligned in a line or curve are more related to each other than the ones that are not.
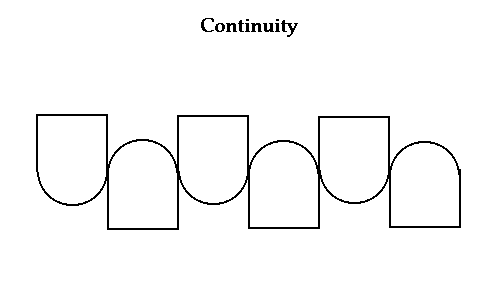
This is another useful way to highlight the relations between the elements in your design. You can arrange the objects in a line or a curve to influence the users’ understanding of how to interact with the elements in your design.

Closure
When we look at some visual pattern where a lot of different elements are arranged together, our brain tends to look for the one single element that should be shaped out of the smaller ones.

It’s like when you look at the Dodge Ram logo, you tend to see the ram pictured there, but if you look a few seconds longer, you’ll note that this is a complex arrangement of different small elements.
Focal Point
Focal point works like us, ha-ha. We all want to stand out from the crowd and to be noted. Well, that’s what focal point helps you to do while you design your interfaces.
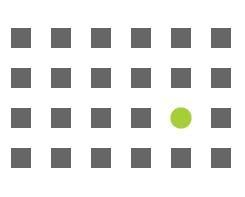
It says that when one particular element looks like precisely the opposite of any other element in the arrangement, we seem to note it much faster and pay more attention to it. I believe that applying it to the CTA buttons and elements should be crucial for any landing page design.
Bottom line
Our brain is a fascinating thing that helps us analyze the world around us and see patterns, arrangements, and complex shapes. When you work as a designer of interfaces, using the gestalt principles and applying them to your projects is the most fantastic idea you can have. Manipulating the users’ behaviors and making sure they do what they need to do, are the best things a designer can work on.

Read Also
7 Web Design Trends To Hold On To In 2018
How Web Designers Save Money: A DepositPhotos Deal Included!
Top 10 Web Design Magazines for Graphic & Web Designers
The Best Web Design Tools Of 2018
How to Market Your WordPress Web Design Business for More Exposure
Get more to your email
Subscribe to our newsletter and access exclusive content and offers available only to MonsterPost subscribers.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.